AGV and AMR, the Key to Intelligent Automation
Revolutionising Industry: AGVs – Automated Guided Vehicles and AMR – Autonomous Mobile Robots
Today’s manufacturing and logistics landscape is undergoing a dynamic transformation thanks to advances in automation technologies. Two of these technologies, Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR), have become the pillars of this transformation. They are crucial for automating various tasks in warehousing, manufacturing and logistics. Despite their similarities, understanding their differences is key to choosing the right automation solution.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): Precision and Efficiency on Fixed Routes
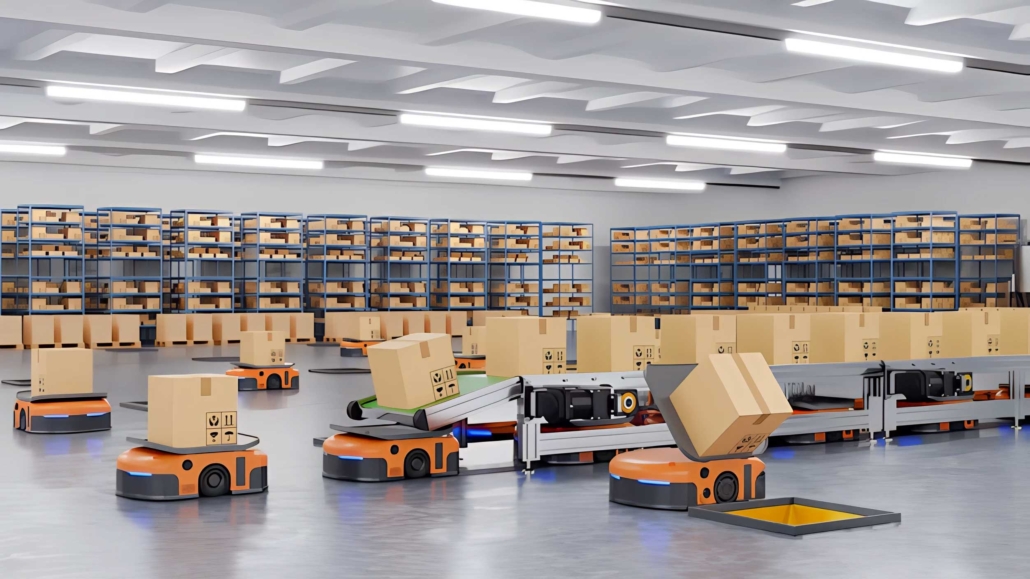
AGVs are robotic vehicles programmed to follow a fixed route within a facility. They typically rely on markers or wires in the ground, or use vision, magnets or lasers to follow a pre-set route. These routes are usually predetermined and only change if they are reprogrammed or reconfigured. This makes AGVs excellent for repetitive tasks and simple applications where the environment remains relatively constant, such as transporting goods along a production line.
The strength of AGVs lies in their ability to perform tasks with high precision and efficiency, providing a reliable and cost-effective solution for moving materials in a controlled environment. They minimise errors, reduce labour costs and improve safety by reducing accidents associated with manual handling.
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR): Intelligence and Adaptability in Dynamic Environments
While AGVs have been around for decades, Autonomous Mobile Robots are a more recent development in the field of automation. AMRs are characterised by their higher degree of autonomy, ability to navigate and make independent decisions based on their environment. Equipped with advanced sensors, cameras and artificial intelligence, AMRs can sense their environment, map their surroundings and dynamically redirect themselves if they encounter an obstacle.
AMRs are especially useful in complex and changing environments where routes must be adjusted frequently. This makes them highly adaptable and flexible, suitable for highly reactive and versatile applications. AMRs can also learn from their experiences, optimising their performance through machine learning algorithms.
AGV and AMR: Complementary Technologies for Industry 4.0
Choosing between an AGV and an AMR comes down to analysing your specific needs, assessing the nature of your operating environment and understanding the tasks you need to automate. An AMR might be ideal if the work requires high flexibility and adaptability, such as in a dynamic warehouse environment. Conversely, for structured and repetitive tasks in a controlled environment, an AGV would be more appropriate.
In reality, the choice is not always binary, and a combination of AGVs and AMR can be deployed to maximise the efficiency and effectiveness of your operations. They are not competing technologies, but complementary solutions designed to address different scenarios in the Industry 4.0 era.
Both AGVs and AMR significantly automate logistics and manufacturing processes, increasing productivity, reducing costs and improving safety opportunities. Understanding their unique strengths and potential applications is crucial for companies looking to harness the full potential of automation technologies in their operations.
Driving Intelligent Automation with Industrial IT Solutions
AMRs rely on a complex combination of sensors and decision making, complex route planning, machine learning and precise navigation. AGVs, on the other hand, focus on precise navigation along fixed routes, support for multitasking tasks and simplified maintenance and safety.
AIE510-ONX
Fanless AI system with NVIDIA® Jetson Orin™ NX (16GB, 100 TOPS), 8-core Arm Cortex-A78AE CPU, Ampere GPU with 32 Tensor Cores, LPDDR5 memory, expansion options, and Temp from -25°C to +60°C.
AIE100-ONA
Edge AI fanless system with NVIDIA® Jetson Orin™ Nano (up to 1024 Ampere cores and 32 Tensor Cores), up to 8GB on-board LPDDR5 memory, M.2 and PCIe expansion options, and operating temperature from -20°C to +50°C.
PE2101N
Edge AI fanless system with NVIDIA® Jetson Orin™ Nano (up to 1024 Ampere cores and 32 Tensor Cores), up to 8GB on-board LPDDR5 memory, M.2 and PCIe expansion options, and operating temperature from -20°C to +50°C.
PE2100N
Rugged fanless intelligent edge AI system with NVIDIA Jetson™ AGX Orin™, up to 275 TOPS, dual LAN, quad PoE LAN, multiple expansion slots, wide power input (9-36VDC), and operating temperature from -25°C to 55°C.
PE1102N
Rugged Edge AI system with NVIDIA® Jetson™ Orin™ Nano™, supports up to four GMSL2 cameras, designed for demanding AI applications such as autonomous vehicles, robotics, industrial automation, and video surveillance.
PE1101N
Rugged fanless intelligent edge AI system with NVIDIA Jetson™ Orin™ NX or Orin™ Nano, up to 100 TOPS, GbE LAN, dual M.2 slots for expansion, wide power input (12-24VDC), and operating temperature from -25°C to 55°C.
PE1100N
Rugged fanless intelligent edge AI system with NVIDIA Jetson™ Orin™ NX or Orin™ Nano, up to 100 TOPS, GbE LAN, dual M.2 slots for expansion, wide power input (12-24VDC), and operating temperature from -25°C to 55°C.
PE1000N
Intelligent edge AI system with NVIDIA Jetson™ Nano™, TX2 NX, and Xavier™ NX, fanless design, dual LAN, HDMI, multiple M.2 slots, mini PCIe, dual SIM, built-in Wi-Fi & BT, LTE-ready, AEM support, and wide power input (12-24V).