NB-IoT vs LTE-M Which is the best technology for your IoT project?
Differences between NB-IoT and LTE-M: Which is the best technology for your IoT project?
 NB-IOT and LTE-M are two Low Power Wide Area (LPWA) technologies developed for IoT applications. Both are low-bandwidth cellular communications protocols that connect devices that need to transmit data to the internet, at low cost and with high battery life.
NB-IOT and LTE-M are two Low Power Wide Area (LPWA) technologies developed for IoT applications. Both are low-bandwidth cellular communications protocols that connect devices that need to transmit data to the internet, at low cost and with high battery life.
In the world of the Internet of Things (IoT), sensors play an essential role in collecting and transmitting valuable data. To connect these sensors to cellular networks, two emerging technologies stand out: NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT) and LTE-M1 or LTE Cat-M1 (Long Term Evolution for Machines).
We show you the differences between these two technologies to help you choose the one that best suits your IoT sensor applications.
Translated with DeepL.com (free version)
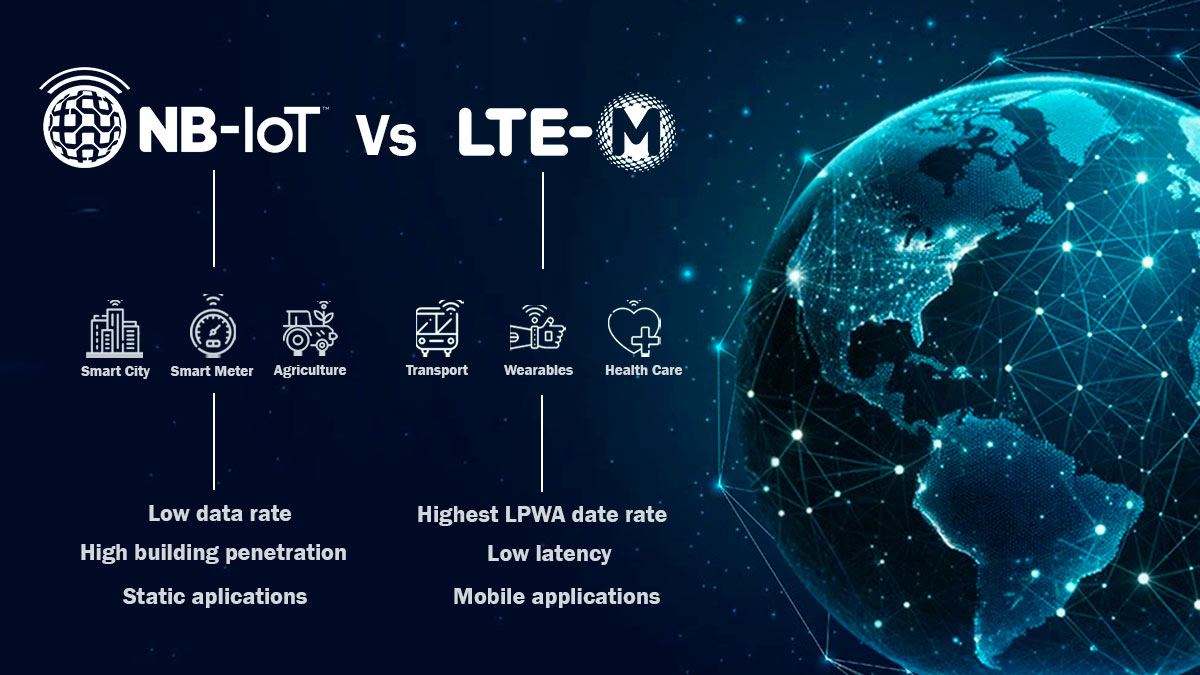
NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT)
NB-IoT is a wide-range network technology specifically designed for IoT applications that require low power consumption and low-speed connectivity. It uses a narrow bandwidth, allowing it to provide excellent signal penetration through obstacles such as buildings and underground areas. NB-IoT is ideal for IoT sensor applications that require long battery life and reliable connectivity over long distances.
LTE-M1 (Long Term Evolution for Machines)
LTE-M1 , also known as LTE-Cat-M1 , is also a cellular network technology suitable for IoT applications. It offers higher data rates than NB-IoT while maintaining low power consumption. LTE-M1 supports applications that require two-way communication and higher data transfers, such as security systems and vehicle tracking. In addition, LTE-M1 offers better latency than NB-IoT, which is essential for IoT applications that require real-time responses.
Key elements to compare
When choosing between NB-IoT and LTE-M1 for IoT applications, it is critical to consider the specific requirements of each project. Here are some key points to consider for a more detailed comparison:
Coverage map
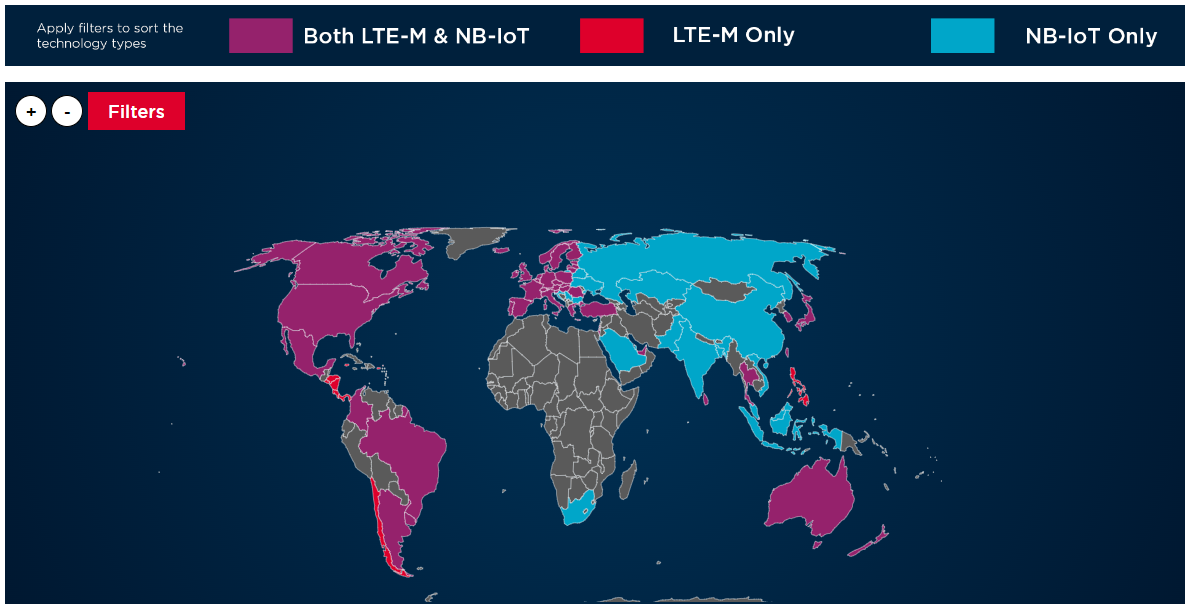
Source: https://www.gsma.com/iot/deployment-map/
Power consumption
Battery life is a crucial factor for IoT sensors, as they typically run on limited power sources, such as batteries or rechargeable batteries. NB-IoT features low power consumption, enabling longer battery life for IoT sensors. This makes it an ideal solution for applications where sensors are deployed in hard-to-reach or low-maintenance locations. Although LTE-M1 consumes slightly more power than NB-IoT, it is still more economical than traditional cellular technologies and offers sufficient battery life for many IoT applications..
Latency and bidirectional connectivity
Latency, the delay between sending a request and receiving a response, is an important issue in IoT applications. LTE-M1 offers better latency than NB-IoT, which means IoT devices can communicate faster and get real-time responses. This can be essential for applications such as security systems or connected medical devices, where fast responsiveness is crucial. In addition, LTE-M1 supports two-way communication, allowing IoT sensors to send real-time information and updates, as well as receive commands. NB-IoT, on the other hand, is optimised for one-way communication, which may be sufficient for certain IoT applications that do not require real-time feedback.
Data rate
Data throughput is an essential factor to consider, depending on the needs of the IoT application. If the application requires sporadic, low-speed data transmission, NB-IoT is a suitable solution. For example, sensors used in environmental monitoring or meter reading applications can operate with low data rates. On the other hand, if the application involves higher data transfers and more information-rich communications, LTE-M1 offers higher data rates, suitable for applications such as vehicle tracking or video surveillance systems.
The cost
LTE-M offers higher throughput and lower latency than NB-IoT, which makes this technology generally more expensive. It is therefore essential to carefully assess the specific needs in order to find the most suitable and cost-effective solution.
In conclusion, the decision between NB-IoT and LTE-M1 depends on the specific requirements of the IoT application.
NB-IoT is ideal for applications requiring low power consumption, long-range connectivity and low data rates.
LTE-M1 is better suited to applications requiring higher data rates, reduced latency and bi-directional communication.
Careful evaluation of these key factors will help in choosing the right technology.